#k8-3 Postgres Client in Kubernetes: Define a Single-Container Pod with Secret-Based Environment Variables
Securely Inject Database Credentials into a Pod Using Kubernetes Secrets
🔒 Role: DevOps Engineer / Kubernetes Admin
⭐ Task:
1️⃣ Postgres Client in Kubernetes: Deploy the client as a Pod.
2️⃣ Single-Container Pod: Ensure only one container runs inside the Pod.
3️⃣ Secret-Based Environment Variables: Use Kubernetes Secrets to inject sensitive data like the database password.
Video Explanation:
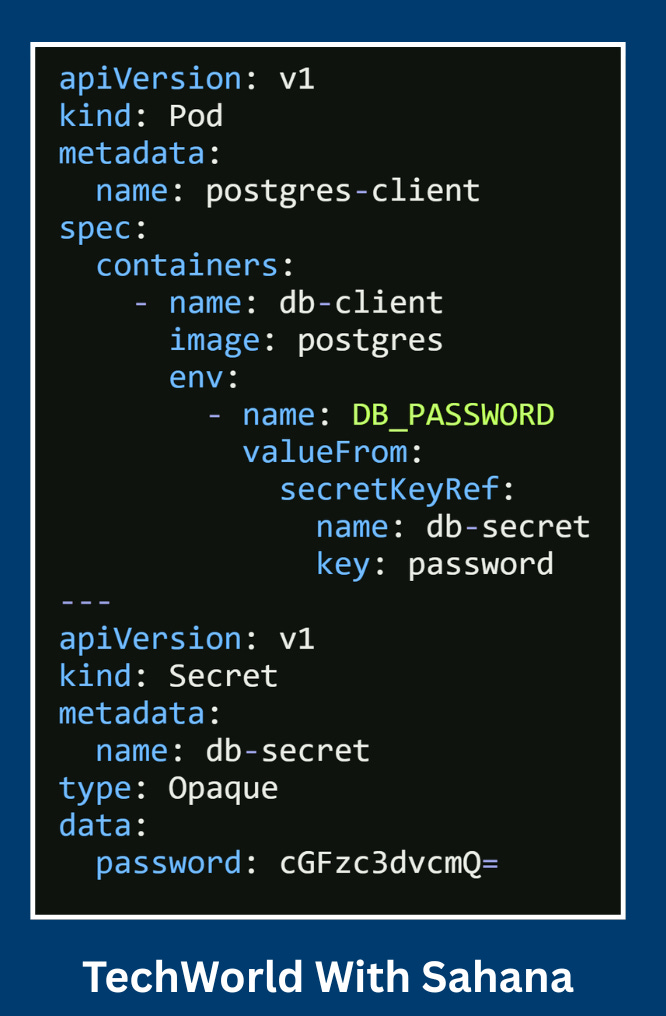
1️⃣In this case, we are using a single container. Let's name it db-client. And it’s using the Postgres image.
containers:
- name: db-client
image: postgres2️⃣ If we write the password directly into the Pod YAML, in the password field, we would expose a sensitive data. To avoid that, we store it securely in a cumulative secret named db-secret.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
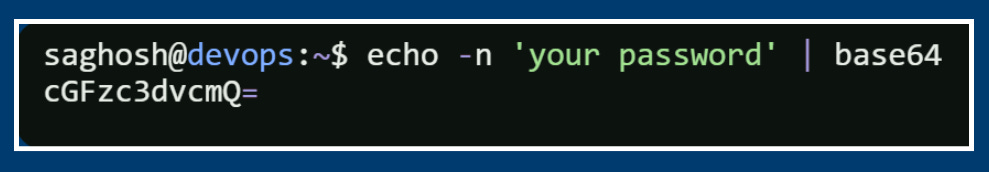
name: db-secret3️⃣And this value right here “cGFzc3dvcmQ=” is a base64 encoded version of Postgres pass. So that means we encoded our password using the below particular echo command.
type: Opaque
data:
password: cGFzc3dvcmQ=4️⃣Now, to use this secret inside the container, we define an environment variable. DB_PASSWORD
env:
- name: DB_PASSWORD5️⃣ And then use the value from the secret key reference field to pull the password value from the db-secret. This way, the actual password stays secure and is only injected into the container at runtime.
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: db-secret
key: password6️⃣Full YAML
Full playlist: Module 2 - Kubernetes Real World YAML Creation
Here’s the flow Step by Step based on YAML:
Kubernetes reads the YAML – It sees two resources:
A
Secretnameddb-secret.A
Podnamedpostgres-client.
Secret created – Kubernetes stores
db-secretof typeOpaquewith the keypasswordcontainingcGFzc3dvcmQ=(Base64 foryour password).Pod scheduled – Kubernetes schedules the
postgres-clientPod on an available node in the cluster.Container pulled – The node pulls the
postgresimage from Docker Hub.Container runs – The container
db-clientstarts inside the Pod.Environment variable injected –
DB_PASSWORDis populated from the Secretdb-secret, keypassword.Kubernetes automatically decodes the Base64 value, so inside the container
DB_PASSWORD=your password.
Pod ready – Kubernetes marks the Pod as Running once the container is up and healthy.
You apply it –
kubectl apply -f postgres-client.yamlcreates both the Secret and the Pod.You verify it –
kubectl get podsensures the Pod is in Running state.kubectl describe pod postgres-clientshows thatDB_PASSWORDcomes from the Secret.
You access it –
kubectl exec -it postgres-client -- bashto enter the container.Inside, you can run
echo $DB_PASSWORDto see the password.
📺 Watch full explanation here:
“10 Kubernetes YAML Real-World Questions” video: